Setting environment variables using agent config
This guide is applicable to Dagster+.
In this guide, we'll walk you through setting environment variables for a Dagster+ Hybrid deployment using the Hybrid agent's configuration.
There are two ways to set environment variables:
- On a per-code location basis, which involves modifying the
dagster_cloud.yamlfile. Note: This approach is functionally the same as setting environment variables using the Dagster+ UI. Values will pass through Dagster+. - For a full deployment and all the code locations it contains. This approach makes variables available for all code locations in a full Dagster+ deployment. As values are pulled from the user cluster, values will bypass Dagster+ entirely.
Prerequisites
To complete the steps in this guide, you'll need:
- A Dagster+ account using Hybrid deployment
- An existing Hybrid agent
- Editor, Admin, or Organization Admin permissions in Dagster+
Setting environment variables for a code location
Setting environment variables require Organization Admin, Admin, or Editor permissions on Dagster+.
If you're a Dagster Editor or Admin, you can only set environment variables for full deployments where you're an Editor or Admin.
You can set environment variables for specific code locations by adding them to your agent's configuration in your project's dagster_cloud.yaml file. The container_context property in this file sets the variables in the agent's environment.
This approach is functionally the same as setting environment variables using the Dagster+ UI.
How container_context is configured depends on the agent type. Click the tab for your agent type to view instructions.
- Amazon ECS agents
- Docker agents
- Kubernetes agents
Using the container_context.ecs.env_vars and container_context.ecs.secrets properties, you can configure environment variables and secrets for a specific code location.
# dagster_cloud.yaml
locations:
- location_name: cloud-examples
image: dagster/dagster-cloud-examples:latest
code_source:
package_name: dagster_cloud_examples
container_context:
ecs:
env_vars:
- DATABASE_NAME=testing
- DATABASE_PASSWORD
secrets:
- name: "MY_API_TOKEN"
valueFrom: "arn:aws:secretsmanager:us-east-1:123456789012:secret:FOO-AbCdEf:token::"
- name: "MY_PASSWORD"
valueFrom: "arn:aws:secretsmanager:us-east-1:123456789012:secret:FOO-AbCdEf:password::"
secrets_tags:
- "my_tag_name"
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
container_context.ecs.env_vars | A list of keys or key-value pairs. If a value is not specified, it pulls from the agent task. E.g., FOO_ENV_VAR = foo_value, BAR_ENV_VAR = agent task value. |
container_context.ecs.secrets | Individual secrets using the ECS API structure. |
container_context.ecs.secrets_tags | A list of tag names; secrets tagged with these in AWS Secrets Manager will be environment variables. The variable name is the secret name, the value is the secret's value. |
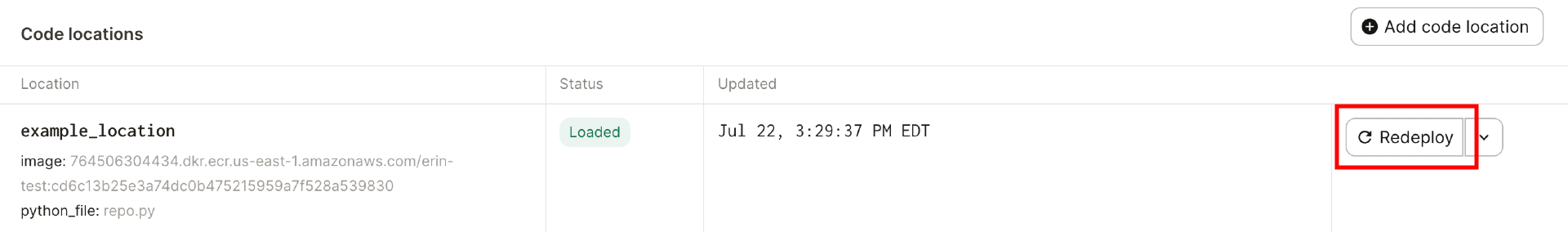
After you've modified dagster_cloud.yaml, redeploy the code location in Dagster+ to apply the changes:
Using the container_context.docker.env_vars property, you can include environment variables and secrets in the Docker container associated with a specific code location. For example:
# dagster_cloud.yaml
locations:
- location_name: cloud-examples
image: dagster/dagster-cloud-examples:latest
code_source:
package_name: dagster_cloud_examples
container_context:
docker:
env_vars:
- DATABASE_NAME
- DATABASE_USERNAME=hooli_testing
The container_context.docker.env_vars property is a list, where each item can be either KEY or KEY=VALUE. If only KEY is specified, the value will be pulled from the local environment.
After you've modified dagster_cloud.yaml, redeploy the code location in Dagster+ to apply the changes:

Using the container_context.k8s.env_vars and container_context.k8s.env_secrets properties, you can specify environment variables and secrets for a specific code location. For example:
# dagster_cloud.yaml
locations:
- location_name: cloud-examples
image: dagster/dagster-cloud-examples:latest
code_source:
package_name: dagster_cloud_examples
container_context:
k8s:
env_vars:
- database_name # value pulled from agent's environment
- database_username=hooli_testing
env_secrets:
- database_password
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
env_vars | A list of environment variable names to inject into the job, formatted as KEY or KEY=VALUE. If only KEY is specified, the value will be pulled from the current process. |
env_secrets | A list of secret names, from which environment variables for a job are drawn using envFrom. For more information, see the Kubernetes. |
After you've modified dagster_cloud.yaml, redeploy the code location in Dagster+ to apply the changes:

Setting environment variables for full deployments
If you're a Dagster Editor or Admin, you can only set environment variables for full deployments where you're an Editor or Admin.
Setting environment variables for a full deployment will make the variables available for all code locations in the full deployment. Using this approach will pull variable values from your user cluster, bypassing Dagster+ entirely.
Click the tab for your agent type to view instructions.
- Amazon ECS agents
- Docker agents
- Kubernetes agents
To make environment variables accessible to a full deployment with an Amazon ECS agent, you'll need to modify the agent's CloudFormation template as follows:
-
Sign in to your AWS account.
-
Navigate to CloudFormation and open the stack for the agent.
-
Click Update.
-
Click Edit template in designer.
-
In the section that displays, click View in Designer. The AWS template designer will display.
-
In the section displaying the template YAML, locate the
AgentTaskDefinitionsection: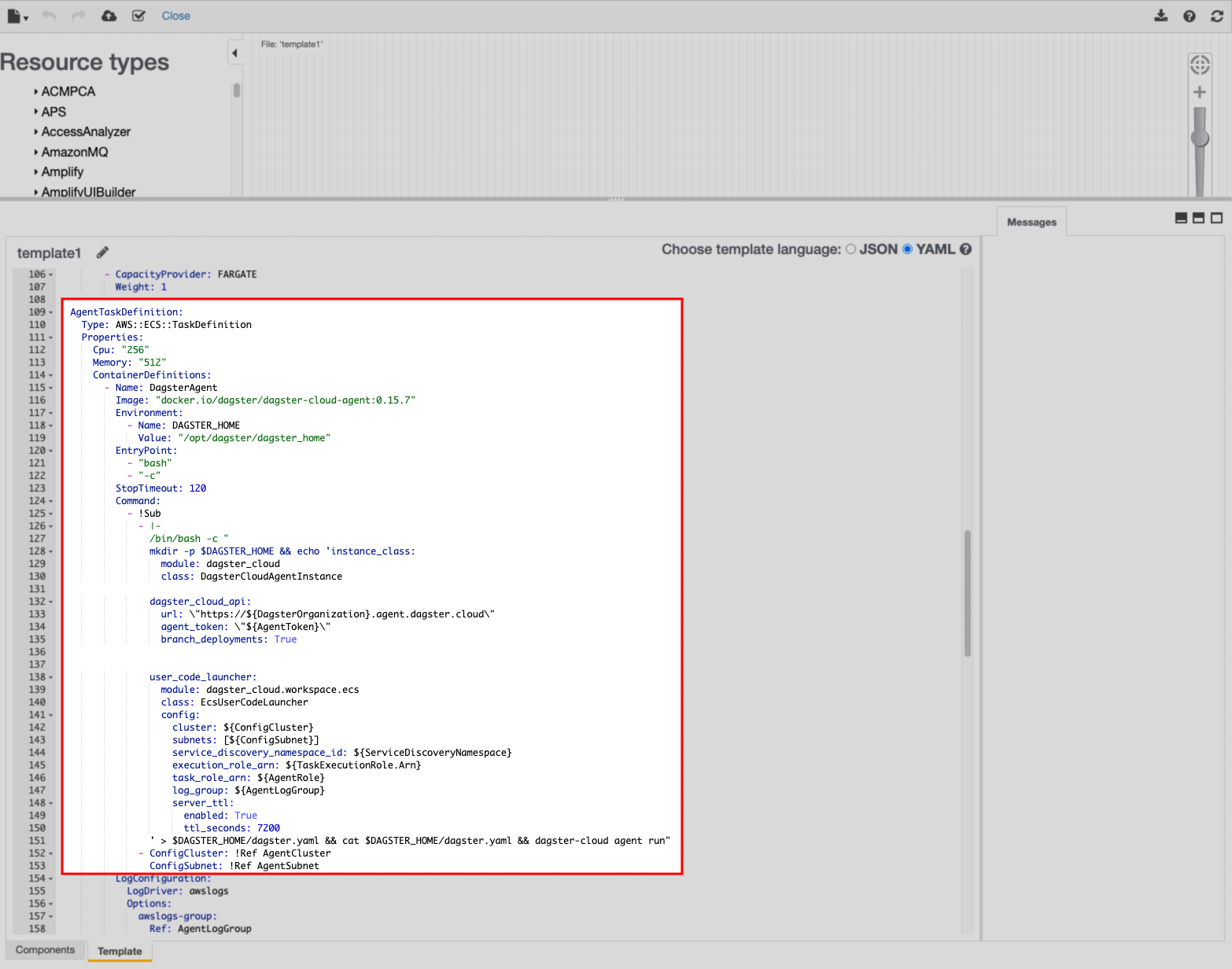
-
In the
user_code_launcher.configportion of theAgentTaskDefinitionsection, add the environment variables as follows:user_code_launcher:
module: dagster_cloud.workspace.ecs
class: EcsUserCodeLauncher
config:
cluster: ${ConfigCluster}
subnets: [${ConfigSubnet}]
service_discovery_namespace_id: ${ServiceDiscoveryNamespace}
execution_role_arn: ${TaskExecutionRole.Arn}
task_role_arn: ${AgentRole}
log_group: ${AgentLogGroup}
env_vars:
- SNOWFLAKE_USERNAME=dev
- SNOWFLAKE_PASSWORD ## pulled from agent environment
' > $DAGSTER_HOME/dagster.yaml && cat $DAGSTER_HOME/dagster.yaml && dagster-cloud agent run" -
When finished, click the Create Stack button:
-
You'll be redirected back to the Update stack wizard, where the new template will be populated. Click Next.
-
Continue to click Next until you reach the Review page.
-
Click Submit to update the stack.
To make environment variables accessible to a full deployment with a Docker agent, you'll need to modify your project's dagster.yaml file.
In the user_code_launcher section, add an env_vars property as follows:
# dagster.yaml
user_code_launcher:
module: dagster_cloud.workspace.docker
class: DockerUserCodeLauncher
config:
networks:
- dagster_cloud_agent
env_vars:
- SNOWFLAKE_PASSWORD # value pulled from agent's environment
- SNOWFLAKE_USERNAME=dev
In env_vars, specify the environment variables as keys (SNOWFLAKE_PASSWORD) or key-value pairs (SNOWFLAKE_USERNAME=dev). If only KEY is provided, the value will be pulled from the agent's environment.
To make environment variables available to a full deployment with a Kubernetes agent, you'll need to modify and upgrade the Helm chart's values.yaml.
-
In
values.yaml, add or locate theworkspacevalue. -
Add an
envVarsproperty as follows:# values.yaml
workspace:
envVars:
- SNOWFLAKE_PASSWORD # value pulled from agent's environment
- SNOWFLAKE_USERNAME=dev -
In
envVars, specify the environment variables as keys (SNOWFLAKE_PASSWORD) or key-value pairs (SNOWFLAKE_USERNAME=dev). If onlyKEYis provided, the value will be pulled from the local (agent's) environment. -
Upgrade the Helm chart.